What is rapid prototyping?
Rapid prototyping (RP) refers to various processes for the rapid production of prototypes. “Fast model building” makes it possible to produce physical models in just a short time. The models are based on three-dimensional CAD (Computer Aided Design) data. Rapid prototyping is used in a wide variety of industries. Either to accelerate the product development process, test preliminary results or visualize initial ideas. Rapid prototyping also offers more security for the transition to series production.

Benefits of rapid prototyping
- Fast production
- Effective presentation of ideas
- More flexibility and faster adaptability
- Cost and time savings in product development
- Immediate functional and formal testing of functions
- Process and implement improvements faster
- Reducing product development and time to market

How does rapid prototyping work?
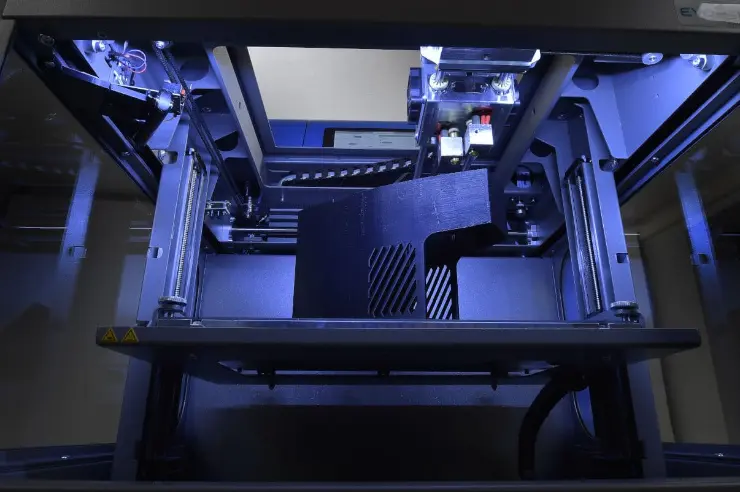
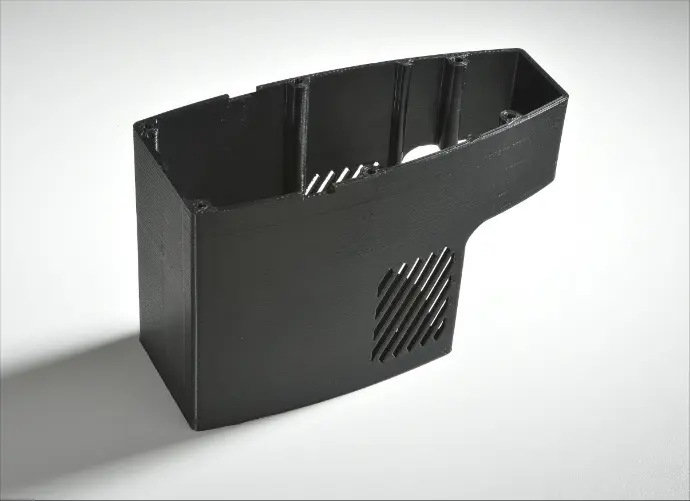
There are several methods for rapid prototyping. 3D printing enables the fastest and most cost-effective prototype production. This is an additive manufacturing technology. The component is manufactured by applying the material layer by layer. The basis for prototype production is CAD (Computer Aided Design) or 3D programming software. The data is read by the 3D printer and transferred to the component. Layers of liquid powder or plate material are placed on top of each other and the model is built up layer by layer. The layers are automatically connected to each other and the prototype is created. This quick process leads to enormous cost and time savings throughout the entire manufacturing process. Prototypes are therefore available quickly. Depending on the size and number of models, the time can vary, but typically prototypes can be made in just a few hours. With the help of this process, not only prototypes can be produced; in certain industries, components for series production or spare parts can also be manufactured.
Well-known rapid prototyping processes
Selective laser sintering (SLS)
With selective laser sintering, the models are produced using a laser beam. Various plastic-like powdery materials such as alumides or polyamides are melted together.
Stereolithography (SLA)
In this rapid prototyping process, the workpiece is lowered into a liquid photopolymer. A laser then moves over the starting material step by step until the desired shape is achieved. SLA is an extremely precise process that can be used to create smooth surfaces.
Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF)
This rapid prototyping process is a fusion deposition process. Here the object is made layer by layer from a meltable plastic. The plastic ABS is usually used, which is very durable and robust.
Selective laser melting (SLM)
Selective laser melting is a rapid prototyping process used for the production of metal parts. The components are again constructed using the layering process.
3D printing (3DP)
With 3D printing, the model is made from a plaster-like powder and applied layer by layer. The layers adhere to one another using a binder and fuse together. 3D printing is a very cost-effective and particularly fast process.
Different versions of rapid prototypes
Design prototype
A design prototype is being manufactured so that aesthetic and ergonomic features can be tested initially.
Concept prototype
The prototype is used to illustrate an idea or a specific concept.
Functional prototype
A functional prototype already has the most important functional properties that the later end product should also have. Mechanical, electrical, acoustic or thermal functions can be tested and checked using the functional prototype.
Geometric prototype
This type of prototype is a dimensionally accurate model that is used for initial assembly and usage tests. This is used to test and check the fit and tolerances.
More efficiency in prototype construction with 3D printing
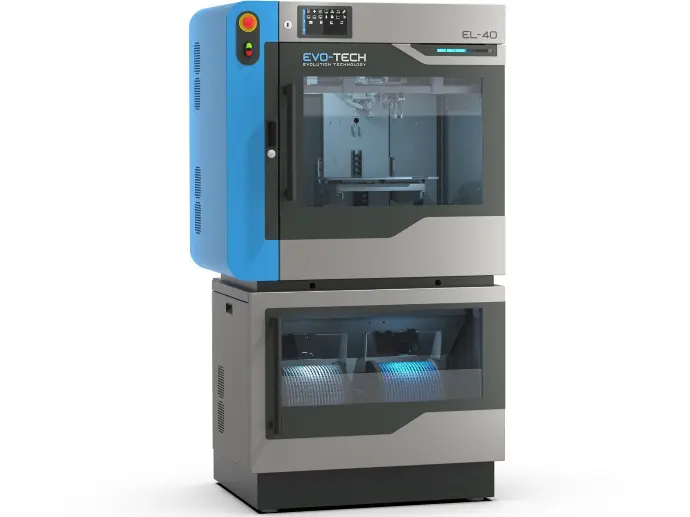

3D printer EL-40
Enables the creation of parts up to 270 x 200 x 210mm (W x D x H) with extremely low operating costs and an open system for filaments.
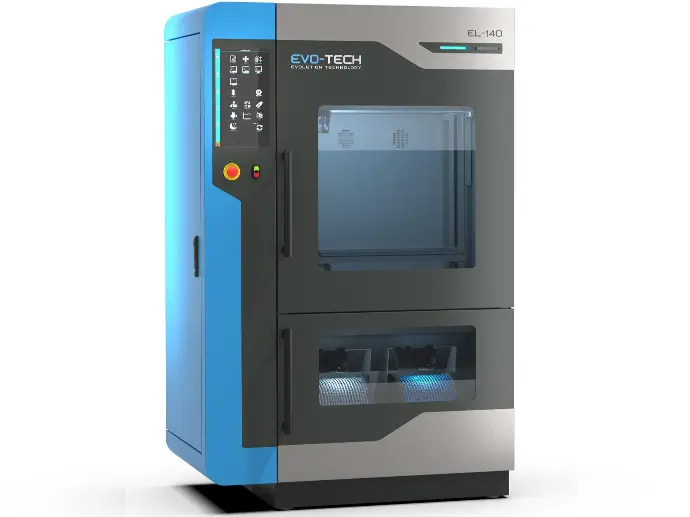

3D printer EL-140
Enables simultaneous printing of multiple parts and the processing of large quantities of material up to a size of 570 x 450 x 570 mm (W x D x H).
